Make Powerwall 3 Wiring Connections
Make Powerwall 3 AC Power Connections
Connect Powerwall 3 to the appropriate breaker size
depending on the desired power / current output (configured in Tesla One):
| Maximum Continuous Current | Power Output (AC) | Breaker (Overcurrent Protection) |
|---|---|---|
48 A On-grid | 11.5 kW On-grid | 80 A* |
| 48 A | 11.5 kW (default) | 60 A |
| 41.7 A | 10 kW | 60 A |
| 31.7 A | 7.6 kW | 40 A |
| 24 A | 5.8 kW | 30 A |
*Powerwall 3 can only provide 15.4 kW when off-grid and when there is sufficient solar; when the system is on-grid, and/or when solar production is insufficient, Powerwall 3 will provide 11.5 kW. If enabling this feature, Powerwall 3 must be installed with an 80 A breaker and appropriately sized conductors.
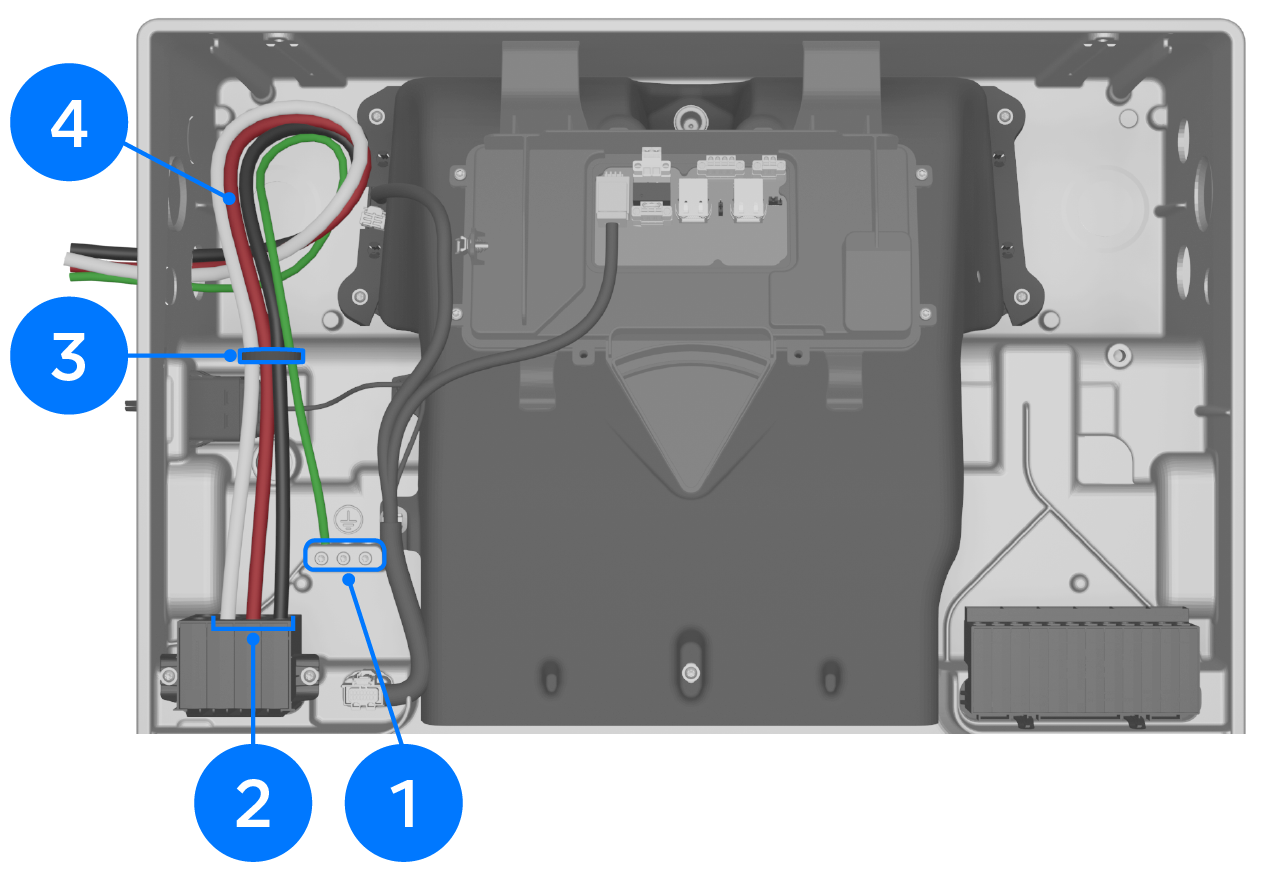
| 1 | Ground terminals: 12-4 AWG (4-25 mm2), torque to 35 in-lb with Torx T20 |
| 2 | N / L2 / L1: 10-4 AWG (6-25 mm2), use up to 4.5 mm (3/16 inch) cabinet / electronics tip screwdriver |
| 3 | Gather conductors in provided cable tie |
| 4 | Leave a service loop |
CAUTION
If using a fuse
as the Powerwall 3 overcurrent protection
device, it must be a Class RK1 Fast Acting fuse. Use one of the following fuses
or equivalent:
| Fuse Type | Manufacturer | Part Number |
|---|---|---|
| 80 A Fast-Acting Fuse, Class RK1, >= 250VAC, CLF | Littelfuse | KLNR080 |
| Eaton / Bussmann | KTN-R-80 | |
| Mersen / Ferraz Shawmut | A2K80R | |
| 60 A Fast-Acting Fuse, Class RK1, >= 250VAC, CLF | Littelfuse | KLNR60 |
| Eaton / Bussmann | KTN-R-60 | |
| Mersen / Ferraz Shawmut | A2K60R | |
| 40 A Fast-Acting Fuse, Class RK1, >= 250VAC, CLF | Littelfuse | KLNR40 |
| Eaton / Bussmann | KTN-R-40 | |
| Mersen / Ferraz Shawmut | A2K40R | |
| 30 A Fast-Acting Fuse, Class RK1, >= 250VAC, CLF | Littelfuse | KLNR30 |
| Eaton / Bussmann | KTN-R-30 | |
| Mersen / Ferraz Shawmut | A2K350 |
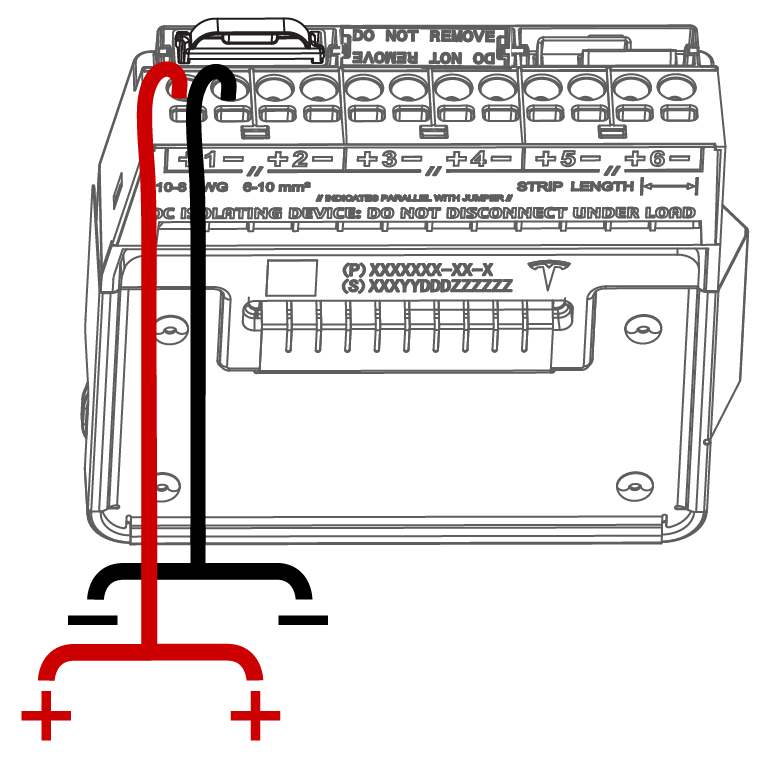
Make Powerwall 3 PV Power Connections
Warning
Turn the Powerwall 3 Enable switch OFF before doing any wiring.
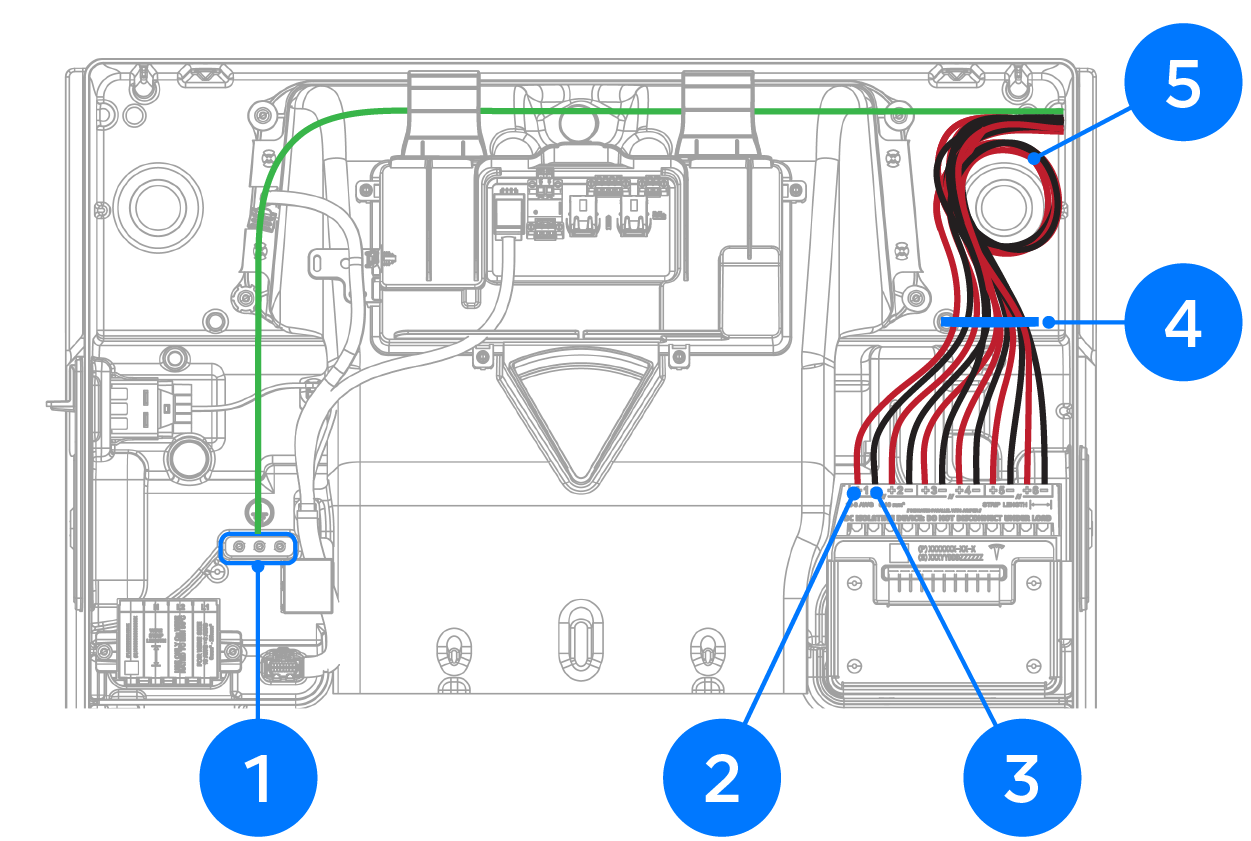
| 1 | Ground terminals: 12-4 AWG (4-25 mm2), torque to 35 in-lb with Torx T20 | |
| 2 | MPPT Positive PV inputs: 10-6 AWG (6-16 mm2) | Use up to 4.5 mm (3/16 inch) cabinet / electronics tip screwdriver |
| 3 | MPPT Negative PV inputs: 10-6 AWG (6-16 mm2) | |
| 4 | Gather conductors in provided cable tie | |
| 5 | Leave a service loop | |
Important Notes on Installing MPPT
Jumpers:
- The jumpers provided in the Powerwall 3 accessory bag can only be used with the Powerwall 3 model they shipped with:
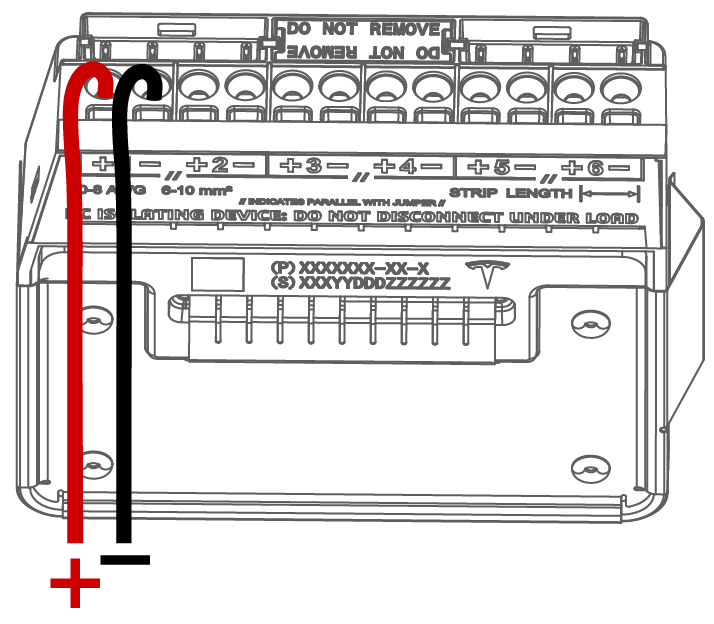
- Jumpers can be used when IMP > 13A. Use jumpers to allow a single MPPT to intake strings with a total IMP up to 26A
- Land the combined circuit (2
strings in parallel = 1 circuit) or string with IMP greater than 13A
in the terminal and connect the jumper from:
- MPPT 1 to MPPT 2
- MPPT 5 to MPPT 6
- MPPT PV inputs 3 and 4 cannot be combined and are closed from the factory
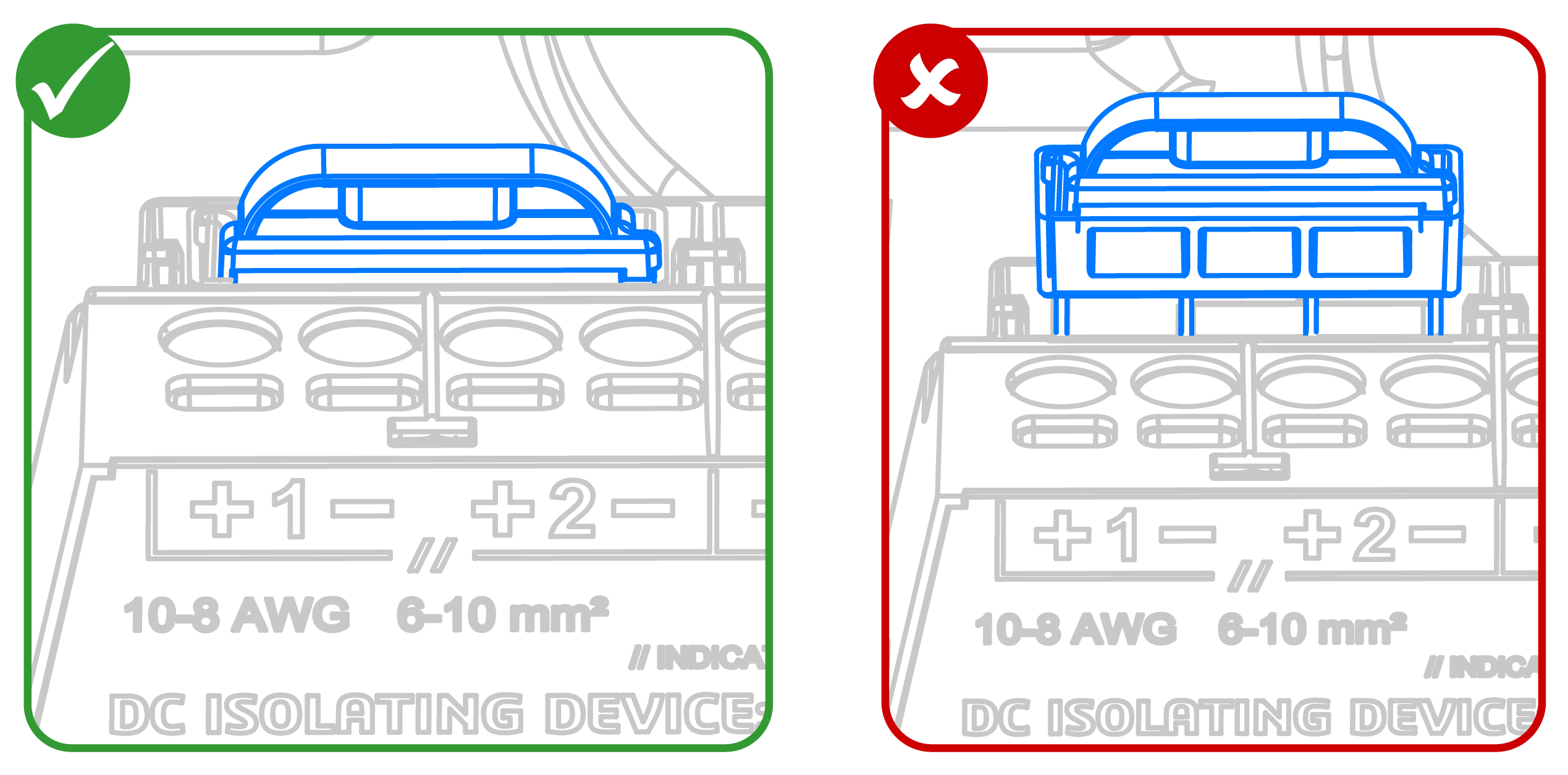
- Do not use jumpers on Solar Roof jobs - you cannot parallel more than two strings so combined circuit IMP will always be less than 13A DC
- Ensure each jumper is fully
seated in the connector!
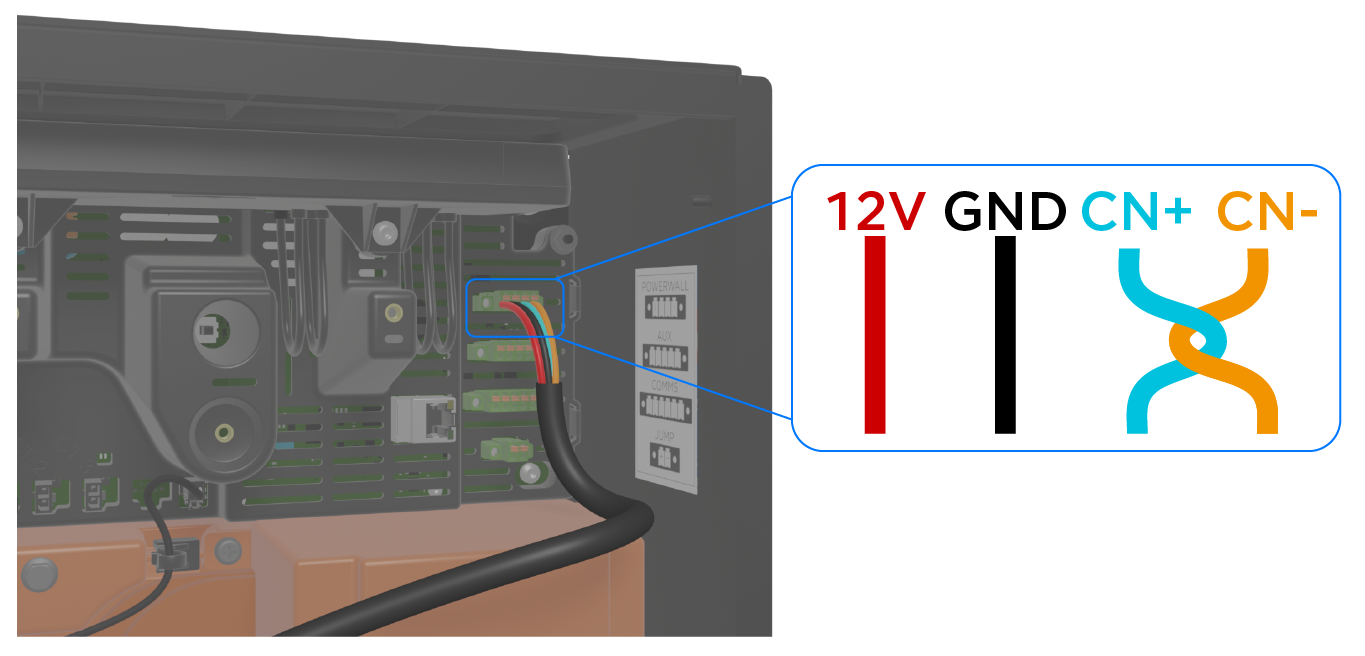
Connect Powerwall 3 to the Backup Switch / Backup Gateway 2 / Gateway 3
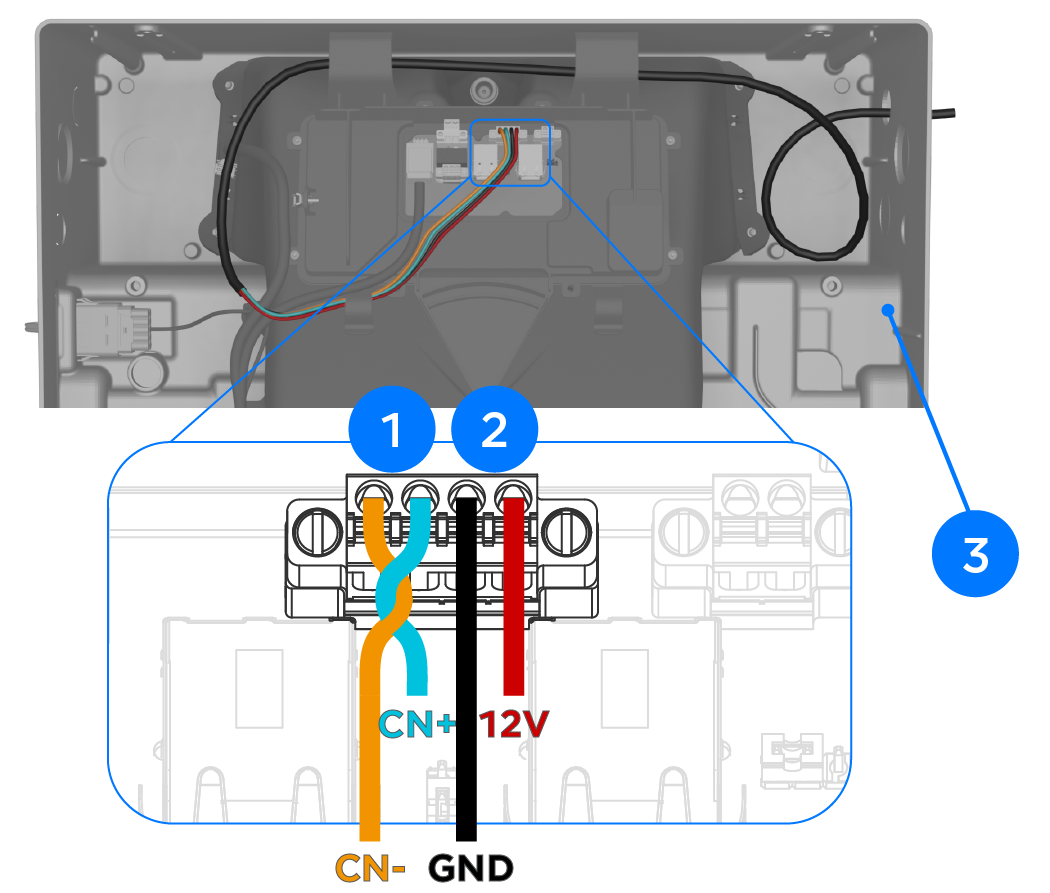
| 1 | CN- (CAN LO): 24-16 AWG (0.2-1.5 mm2) | Use up to 3 mm (3/32 inch) cabinet / electronics tip screwdriver |
| CN+ (CAN HI): 24-16 AWG (0.2-1.5 mm2) | ||
| 2 | GND: 24-16 AWG (0.2-1.5 mm2)* | |
| 12V+: 24-16 AWG (0.2-1.5 mm2)* | ||
| 3 | Leave a service loop | |
*18 AWG is the recommended minimum wire gauge due to potential voltage drop on long wire runs.
Note
CN- and CN+ must be twisted pair.
Install System Shutdown Switch Where Required
CAUTION
The System Shutdown
Switch must be connected to Powerwall 3. Do not connect it to the
Backup Gateway 2 as it will not work.
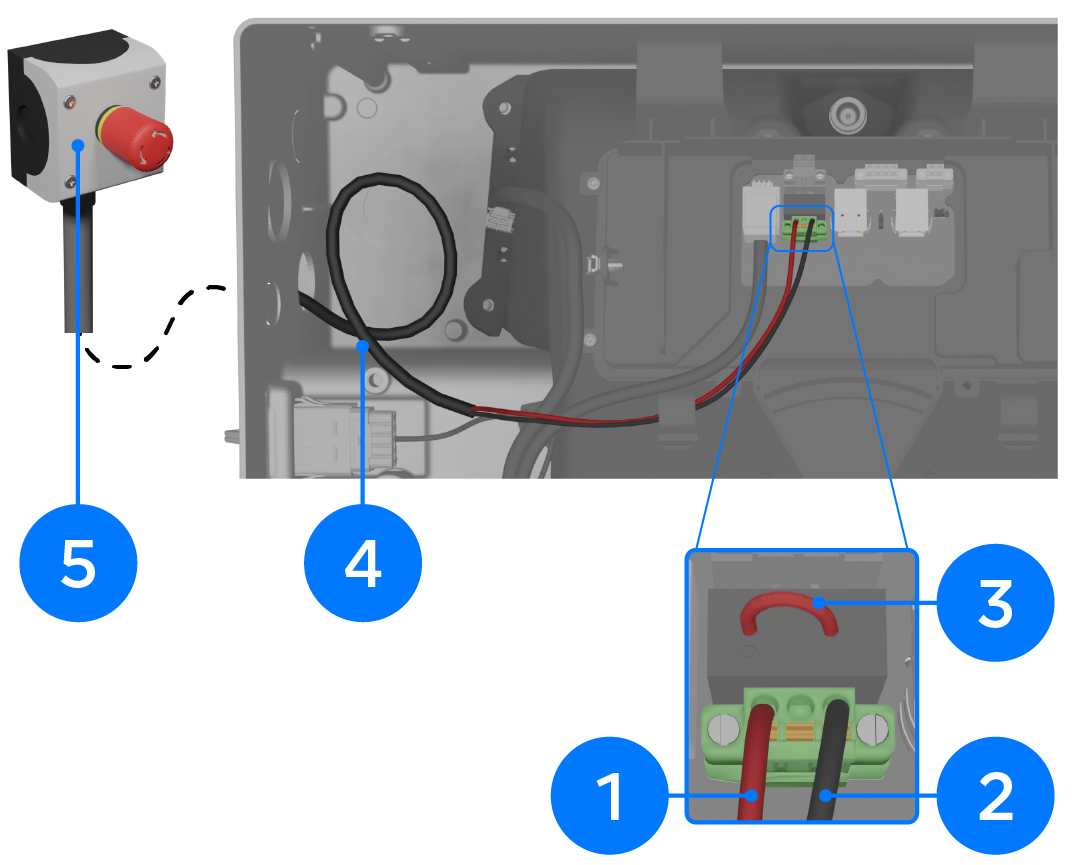
| 1 | Rapid Shutdown IN: 24-16 AWG (0.2-1.5 mm2) | Use up to 3 mm (3/32 inch) cabinet / electronics tip screwdriver |
| 2 | Rapid Shutdown OUT: 24-16 AWG (0.2-1.5 mm2) | |
| 3 | Remove RSD jumper when installing System Shutdown Switch; otherwise, leave installed | |
| 4 | Leave a service loop | |
| 5 | Connect the RSD wiring to a suitable DC switch (see the Powerwall 3 with Backup Gateway 2, Backup Switch, or Gateway 3 installation manual for full details) | |
Note
See Multi-Powerwall 3 Installations for
instructions to connect multiple Powerwall 3 units to a System Shutdown Switch.
Install Ferrite Cores
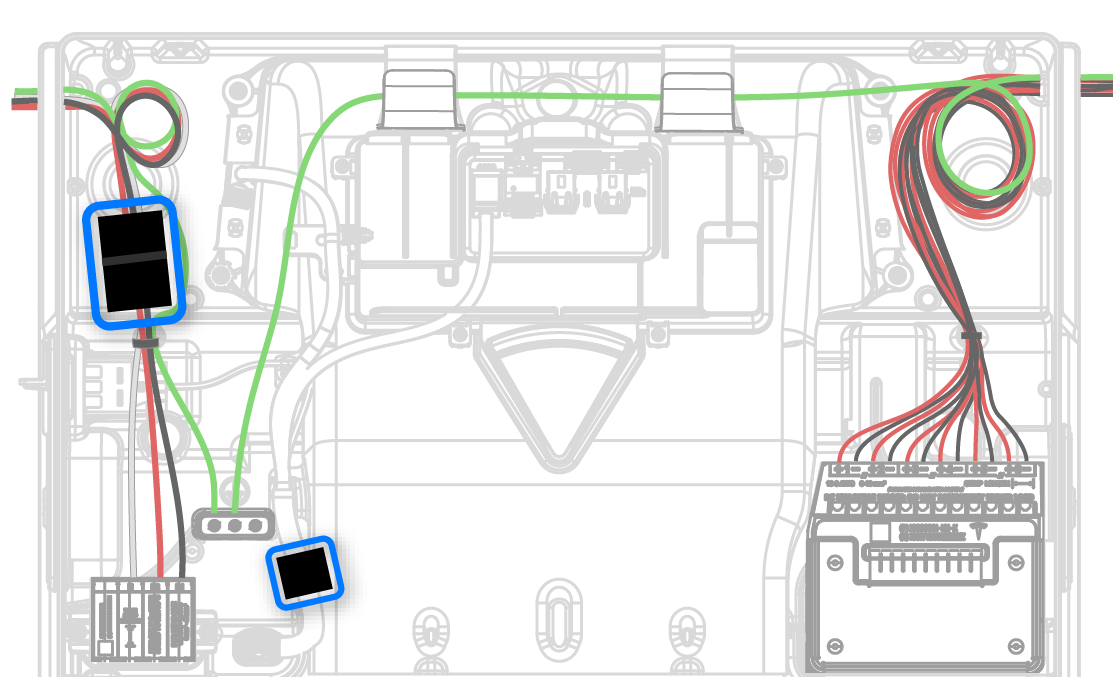
- (1) large clamp-on ferrite core for the AC conductors
- (1) small clamp-on ferrite core for the TACO low voltage harness
CAUTION
Ferrite cores
are fragile; handle with caution.
Note
Ground wires do not need to be
included in the ferrite cores.
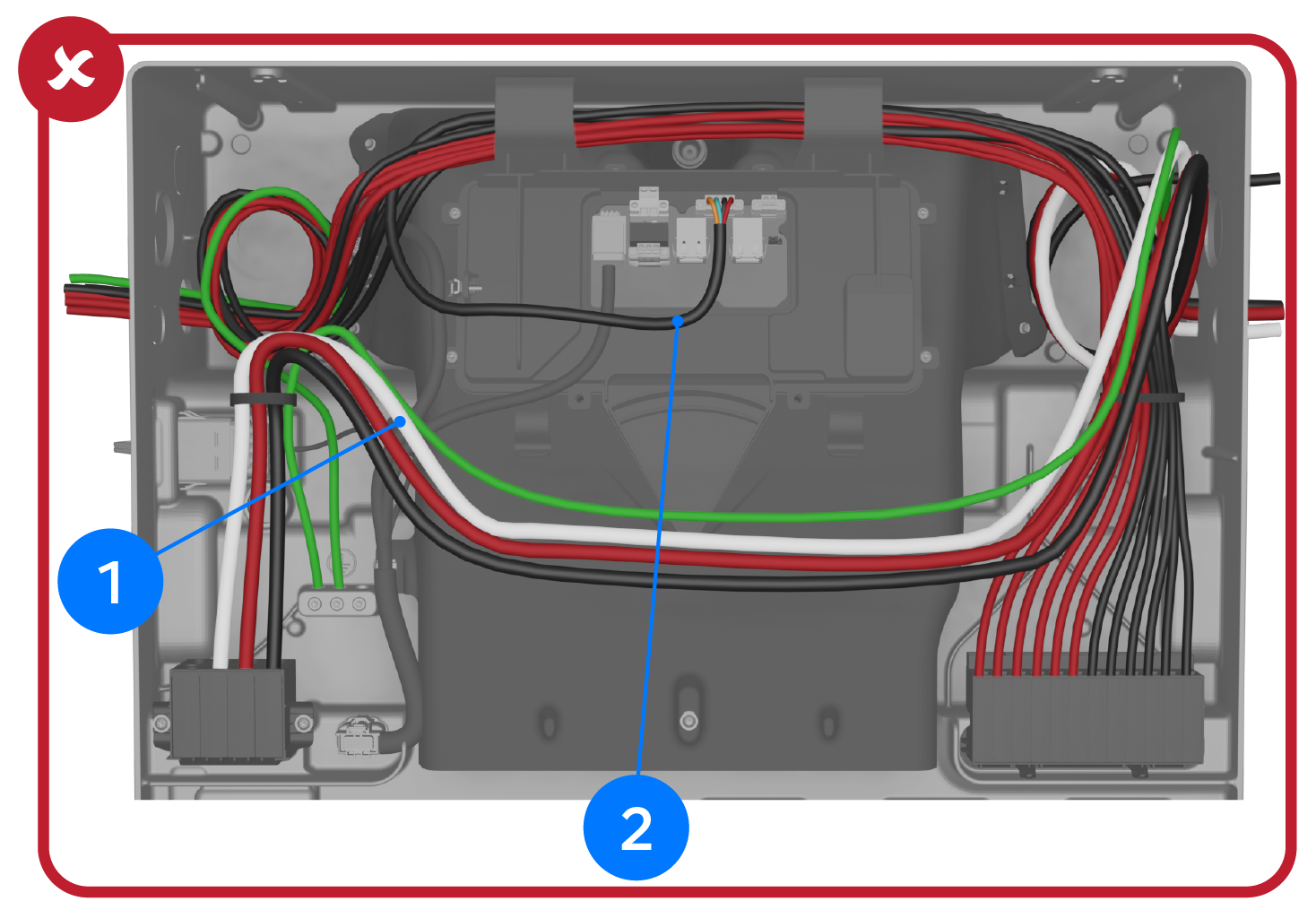
Important Notes on Wire Routing
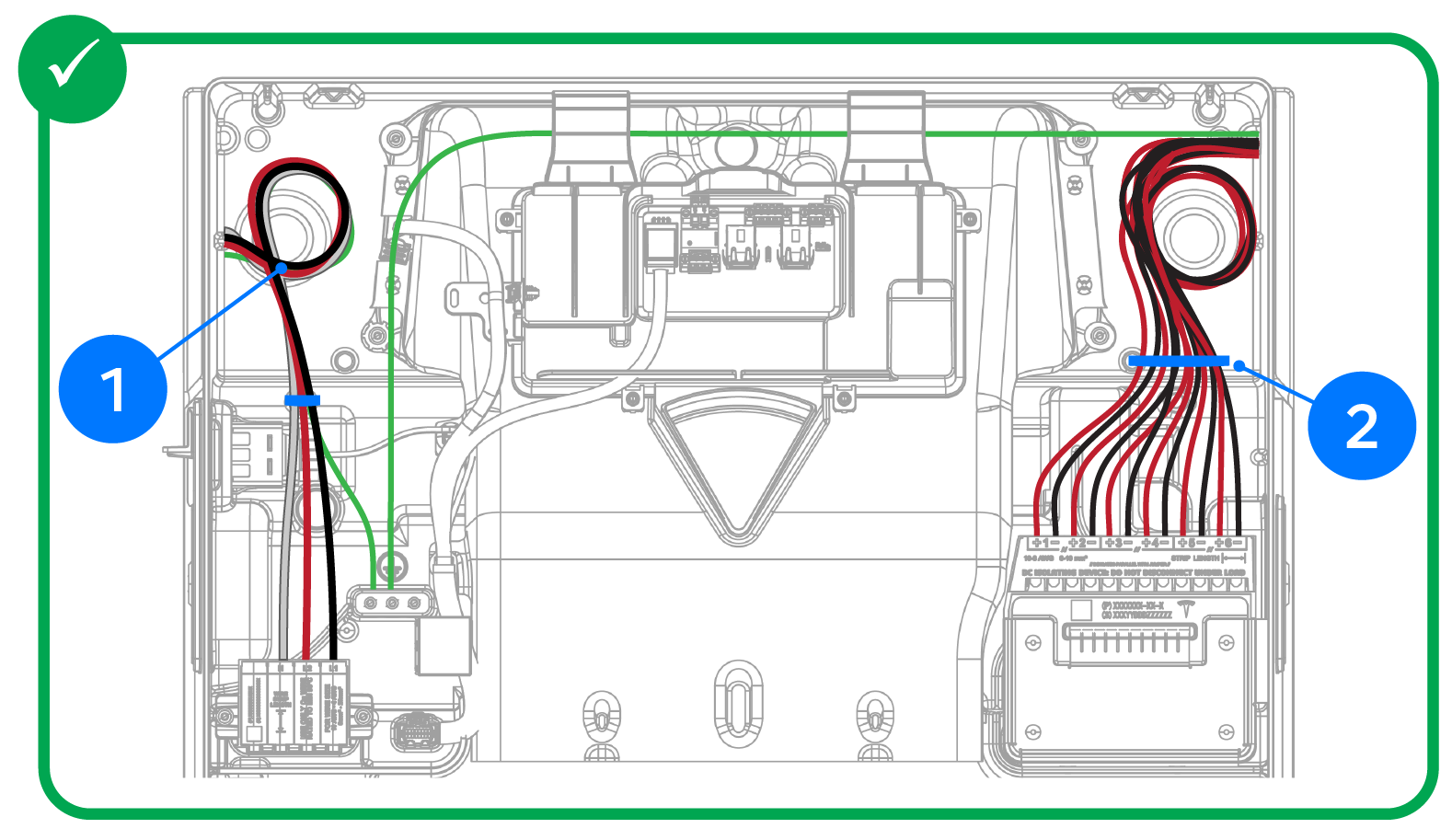
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
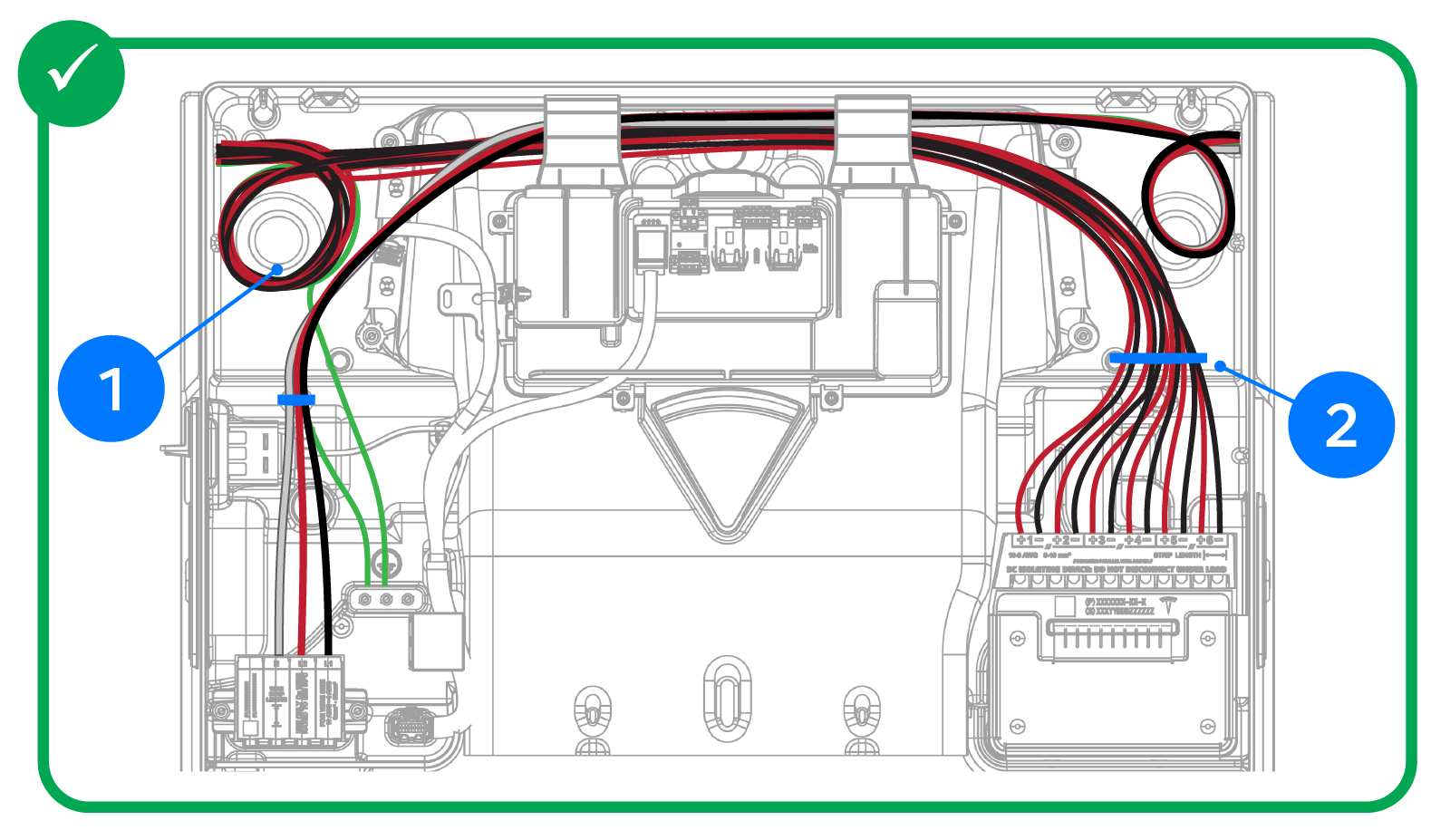
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|